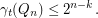login/create account
login/create account
Total Domination number of a hypercube (Solved)
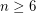 ,
, 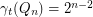 .
.
Here 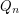 denotes the
denotes the  -dimensional hypercube, i.e. the graph with vertex set
-dimensional hypercube, i.e. the graph with vertex set 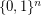 and two vertices adjacent if they differ in exactly one coordinate. A total dominating set of a graph
and two vertices adjacent if they differ in exactly one coordinate. A total dominating set of a graph 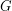 is a set
is a set 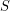 of vertices of
of vertices of 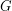 such that every vertex has at least one neighbor in
such that every vertex has at least one neighbor in 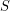 ". The total domination number
". The total domination number 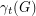 of
of 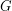 is the cardinality of a minimum total dominating set. A total dominator coloring of a graph
is the cardinality of a minimum total dominating set. A total dominator coloring of a graph 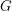 , briefly TDC, is a proper coloring of
, briefly TDC, is a proper coloring of 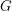 in which each vertex of the graph is adjacent to every vertex of some color class. The total dominator chromatic number
in which each vertex of the graph is adjacent to every vertex of some color class. The total dominator chromatic number 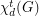 of
of 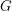 is the minimum number of color classes in a TDC in
is the minimum number of color classes in a TDC in 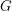 (see [Kaz1]).
(see [Kaz1]).
The following theorems are proved in [Kaz2].
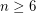 ,
, 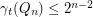 .
. 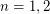 , then
, then 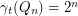 .
. 2. If
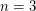 , then
, then 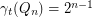 .
. 3. If
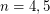 , then
, then 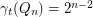 .
. 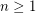 ,
, 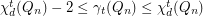 .
. Bibliography
[Kaz1] Adel P. Kazemi, Total dominator chromatic number of a graph, http://arxiv.org/abs/1307.7486.
[Kaz2] Adel P. Kazemi, Total Dominator Coloring in Product Graphs, Utilitas Mathematica (2013), Accepted.
* indicates original appearance(s) of problem.

 Drupal
Drupal CSI of Charles University
CSI of Charles University
The conjecture is false
The conjecture is false and it can be seen that this is so by using a computer program. For example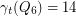 which is not a power of two.
which is not a power of two.
Alternatively we can argue as follows. For any graph we clearly have
we clearly have 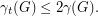 Now the bound by Alon and Spencer states
Now the bound by Alon and Spencer states 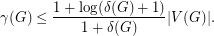 In particular this implies that for any constant
In particular this implies that for any constant 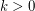 and large enough
and large enough  we have
we have