 login/create account
login/create account
Waring rank of determinant ★★
Author(s): Teitler
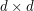 generic matrix?
generic matrix? For simplicity say we work over the complex numbers. The 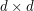 generic matrix is the matrix with entries
generic matrix is the matrix with entries 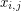 for
for 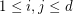 . Its determinant is a homogeneous form of degree
. Its determinant is a homogeneous form of degree 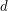 , in
, in 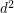 variables. If
variables. If 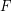 is a homogeneous form of degree
is a homogeneous form of degree 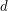 , a power sum expression for
, a power sum expression for 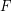 is an expression of the form
is an expression of the form 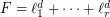 , the
, the 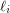 (homogeneous) linear forms. The Waring rank of
(homogeneous) linear forms. The Waring rank of 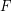 is the least number of terms
is the least number of terms  in any power sum expression for
in any power sum expression for 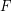 . For example, the expression
. For example, the expression 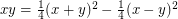 means that
means that 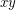 has Waring rank
has Waring rank 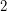 (it can't be less than
(it can't be less than 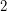 , as
, as 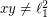 ).
).
The 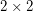 generic determinant
generic determinant 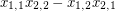 (or
(or 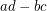 ) has Waring rank
) has Waring rank 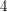 . The Waring rank of the
. The Waring rank of the 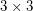 generic determinant is at least
generic determinant is at least 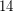 and no more than
and no more than 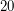 , see for instance Lower bound for ranks of invariant forms, Example 4.1. The Waring rank of the permanent is also of interest. The comparison between the determinant and permanent is potentially relevant to Valiant's "VP versus VNP" problem.
, see for instance Lower bound for ranks of invariant forms, Example 4.1. The Waring rank of the permanent is also of interest. The comparison between the determinant and permanent is potentially relevant to Valiant's "VP versus VNP" problem.
Keywords: Waring rank, determinant
Monochromatic vertex colorings inherited from Perfect Matchings ★★★
Author(s):
 and
and 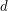 are there bi-colored graphs on
are there bi-colored graphs on  vertices and
vertices and 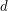 different colors with the property that all the
different colors with the property that all the 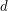 monochromatic colorings have unit weight, and every other coloring cancels out?
monochromatic colorings have unit weight, and every other coloring cancels out? Keywords:
Cycle Double Covers Containing Predefined 2-Regular Subgraphs ★★★
Author(s): Arthur; Hoffmann-Ostenhof
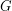 be a
be a 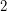 -connected cubic graph and let
-connected cubic graph and let 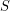 be a
be a 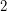 -regular subgraph such that
-regular subgraph such that 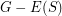 is connected. Then
is connected. Then 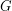 has a cycle double cover which contains
has a cycle double cover which contains 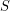 (i.e all cycles of
(i.e all cycles of 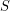 ).
). Keywords:
Monochromatic reachability in arc-colored digraphs ★★★
Author(s): Sands; Sauer; Woodrow
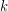 , there exists an integer
, there exists an integer 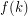 such that if
such that if 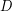 is a digraph whose arcs are colored with
is a digraph whose arcs are colored with 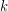 colors, then
colors, then 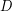 has a
has a 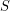 set which is the union of
set which is the union of 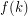 stables sets so that every vertex has a monochromatic path to some vertex in
stables sets so that every vertex has a monochromatic path to some vertex in 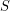 .
. Keywords:
3-Decomposition Conjecture ★★★
Author(s): Arthur; Hoffmann-Ostenhof
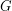 has a decomposition into a spanning tree, a family of cycles and a matching.
has a decomposition into a spanning tree, a family of cycles and a matching. Keywords: cubic graph
Which outer reloids are equal to inner ones ★★
Author(s): Porton
Warning: This formulation is vague (not exact).
 . In other words, simplify this formula.
. In other words, simplify this formula. The problem seems rather difficult.
Keywords:
A diagram about funcoids and reloids ★★
Author(s): Porton
Define for posets with order  :
:
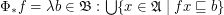 ;
;
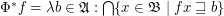 .
.
Note that the above is a generalization of monotone Galois connections (with 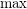 and
and  replaced with suprema and infima).
replaced with suprema and infima).
Then we have the following diagram:
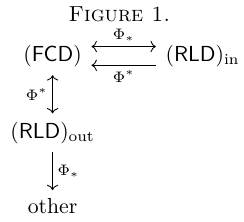
What is at the node "other" in the diagram is unknown.
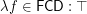 .
. 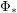 and
and 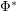 to "other" leads to? Particularly, does repeated applying
to "other" leads to? Particularly, does repeated applying 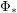 and/or
and/or 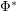 to the node "other" lead to finite or infinite sets?
to the node "other" lead to finite or infinite sets? Keywords: Galois connections

 Drupal
Drupal CSI of Charles University
CSI of Charles University